|
          
~ Pelvic Organ Prolapse ~
Ä Definition:
Cystocele: a downward displacement of the bladder
Cystourethrocele: a cystocele including the urethra as
part of the prolapse organ complex
Uterine Prolapse: descent of uterus and cervix down
the vaginal canal toward the vaginal
introitus
Rectocele: a protrusion of the rectum into the
posterior vaginal lumen
Enterocele: a herniation of the small bowel into the
vaginal lumen
Ä Classification:
Half way system (0-4):
|
Grade |
Description |
|
0 |
Normal position for each side |
|
1 |
Descent halfway to hymen |
|
2 |
Descent to hymen |
|
3 |
Descent halfway past hymen |
|
4 |
Maximum possible descent for each side |
(1-3):
|
Grade |
Description |
|
1 |
Descent beyond hymen |
|
2 |
Descent reaching hymen |
|
3 |
Protruding below vaginal introitus |
ICS classification
Statge 0: No prolapse is demonstrated. Ponts Aa, Ap,
Ba, and Bp are all at –3 cm and either point C or D is between –TVL cm
and –(TVL-2) cm (i.e., the quantitation value for point C or D is ≦
-[TVL-2] cm
Stage 1: The criteria for stage 0 are not met, but
the most distal portion of the prolapse is > 1cm above the level of hymen
(i.e., its quantitaion value is < -1 cm)
Stage II: The most distal portin of the prolapse is ≦
1 cm proximal to or distal to the plane of the hymen (i.e., its quantitation
value is≧
-1 cm but ≦
+1 cm)
Stage III: The most distal portion of the prolapse is
> 1 cm below the plane of the hymen but protrudes no further than 2 cm
less than the total vaginal length in cm (i.e., its quantitaion value is
> +1cm but < +[TVL-2] cm
Sgage IV: Essentially, complete eversion of the total
length of the lower-genital tract is demonstrated. The distal portion of the
prolapse protrudes to at least (TVL-2) cm (i.e., its quantitation value is ≧
[TVL-2] cm). In most instance, the leading edge of stage IV prolapse is the
cervix or vaginal cuff scar.
Ä Symptoms:
A feeling of pressure or that something is protruding from the vagina
A dragging discomfort, which is described as a low backache or feeling of
heaviness and
generally is relieved by lying down, is less noticeable in
the morning, and worsens as the
day progresses, particularly if patients are on their feet
for long periods of time
- Stress incontinence, when urethal hypermobility resulted from loss of ant.
vaginal support
- Voiding difficulty on the condition of large ant. vaginal prolapse
- Inefficient rectal emptying often described as constipation, if rectocele
developing
Ä Examination for
Pelvic Organ Prolapse:
- In the standing position as well as in the standard dorsal lithotomy
position
- PV as well as rectovaginal examination
- Evaluation of pelvic organ prolapse:
j The nature of
prolapse: uterine prolapse? cystocele? rectocele? Enterocele?
k Maximal extent
l Each aspect of
vaginal support: ant.? post.? lat.?
Ä Treatment:
- Asymptomatic prolapse does not need treatment.
- Management for symptomatic prolapse:
j Conservative
Management:
ò Pessary:
1). Individually fitted for each patient
2). Requiring well-estrogenized vagina
For women who are past menopause, it is preferable to
use intravaginal
estrogen cream 4-6 weeks before the pessary is
inserted, because this
makes the pessary more comfortable to wear and
dramatically increases
compliance and promotes long-term use.
3). Regular follow-up to prevent complications (eg. chronic
irritation, erosion,
vesicovaginal fistula
first visit: within 1 week
thereafter: 4-6 months
k Surgical
Management:
Operations for
vaginal prolapse:
- Vaginal hysterectomy
- Manchester/Fothergill operation
- Uteropexy
- Paravaginal defect repair operation
- P-repair
Operations for
complete eversion of the vagina:
- Colpectomy and colpocleisis
- Colpopexy
The standardization of
terminology of female pelvic organ prolpase and pelvic floor dysfuncion. Am J
Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:10
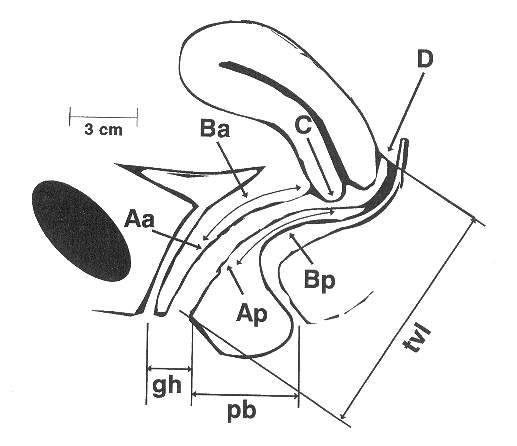
Point Aa: A point located in the midline of the anterior
vaginal wall 3 cm proximal to the external urethral meatus, corresponding to the
approximate location of the "urethrovesical crease," a visible
landmark of variable prominence that is obliterated in many patients.
Point Ba: a point that represents the most distal (i.e.,
most dependent) position of any part of the upper anterior vaginal wall from the
vaginal cuff or anterior vaginal fornix to point Aa.
Point C: A point that represents either the most distal
(i.e., most dependent) edge of the cervix or the leading edge of the vaginal
cuff (hysterectomy scar) after total hysterectomy.
Point D: A point that represents the location of the
posterior fornix (or pouch of Douglas) in a woman who still has a cervix. It
represents the level of uterosacral ligament attachment to the proximal
posterior cervix. It is included as a point of measurement to differentiate
suspensory failure of the uterosacral-cardinal ligament complex from cervical
elongation. Point D is omitted in the absence of the cervix.
Point Bp: A point that represents the most distal (i.e.,
most dependent) position of any part of the upper posterior vaginal wall from
the vaginal cuff or posterior vaginal fornix to point Ap.
Point Ap: A point located in the midline of the posterior
vaginal wall 3 cm proximal to the hymen.
OTHER LANDMARKS AND MEASUREMENTS. The genital hiatus
is measured from the middle of the external urethral meatus to the posterior
midline hymen. If the location of the hymen is distorted by a loose band of skin
without underlying muscle or connective tissue, the firm palpable tissue of the
perineal body should be substituted as the posterior margin for this
measurement. The perineal body is measured from the posterior margin of
the genital hiatus to the midanal opening. Measurements of the genital hiatus
and perineal body are expressed in centimeters. The total vaginal length
is the greatest depth of the vagina in centimeters when point C or D is reduced
to its full normal position.
Filename: Pelvic Organ Prolapse
| 